Respiratory & Air Safety in the Workplace: Risks, Protection, and Best Practices
Air quality in the workplace is often overlooked because the most dangerous threats cannot be seen. Dust, fumes, vapors, and airborne particles may seem harmless at first, but over time they can cause serious health problems for workers across many industries.
Respiratory and air safety is about understanding these risks and taking practical steps to reduce exposure. This guide explains common workplace air hazards, the health effects of poor air protection, and how proper respiratory safety equipment helps create a safer work environment.
What Is Respiratory & Air Safety?
Respiratory and air safety focuses on protecting workers from breathing in harmful substances while on the job. These hazards may come from materials, processes, or environments that release particles or gases into the air.
Unlike physical hazards, airborne risks are often invisible. Workers may not realize they are being exposed until symptoms begin to appear. This makes respiratory protection a critical part of overall workplace safety planning.
Industries commonly affected include construction, manufacturing, warehousing, maintenance, cleaning services, automotive work, and any environment with limited ventilation.

Common Airborne Hazards in the Workplace
Many job sites contain airborne contaminants that can negatively impact health if proper precautions are not taken.
Common hazards include:
- Dust and fine particles from cutting, sanding, or grinding
- Chemical fumes and vapors from solvents, adhesives, or cleaners
- Welding fumes and metal particles
- Mold spores in damp or poorly ventilated spaces
- Smoke and combustion fumes from engines or machinery
Even short-term exposure can cause irritation, while long-term exposure increases the risk of chronic respiratory issues.
For a deeper breakdown of these risks, see our guide on common airborne hazards in the workplace.
Health Risks of Poor Air Protection
Breathing contaminated air does not always cause immediate symptoms, which is why the danger is often underestimated.
Short-term effects may include:
- Throat and lung irritation
- Headaches or dizziness
- Coughing or shortness of breath
- Fatigue and reduced concentration
Long-term exposure can lead to more serious conditions such as:
- Chronic respiratory illness
- Reduced lung function
- Occupational asthma
- Long-term lung damage
Protecting airways early helps reduce these risks before they become permanent health problems.
How Respiratory Protection Helps Reduce Risk
Respiratory protection acts as a barrier between the worker and harmful airborne contaminants. Proper equipment filters particles and gases before they enter the lungs, significantly lowering exposure levels.
Basic face coverings may help with comfort or nuisance dust, but they are not always designed for hazardous environments. Respirators and proper filtration systems are built specifically to handle workplace air risks when used correctly.
Choosing appropriate respiratory protection is one of the most effective steps employers and workers can take to improve safety.
Explore types of respirators and when to use them for workplace environments.
In some environments, air hazards must be monitored before respiratory protection is even used, which is where gas monitors and air detection devices become essential.
Types of Respiratory Protection
These options vary in protection level, but choosing the right one depends on the specific hazard and work conditions.
There are several forms of respiratory protection, each designed for different exposure levels and work conditions.
Common types include:
- Disposable masks for light, short-term exposure
- Half-face respirators that protect the nose and mouth
- Full-face respirators that also shield the eyes and face
- Filters and cartridges designed for specific particles or chemical hazards
The right choice depends on the type of airborne hazard, the duration of exposure, and the work environment.
Choosing the Right Respiratory Protection
Selecting the correct respiratory protection is not one-size-fits-all. Several factors should be considered before choosing equipment.
Key considerations include:
- Type of airborne hazard present
- Concentration and duration of exposure
- Job tasks and movement requirements
- Comfort and proper fit for the worker
Using protection that matches the hazard level helps ensure safety without unnecessary discomfort or restriction.
If filters or cartridges are part of your setup, this guide will help: respirator filters explained
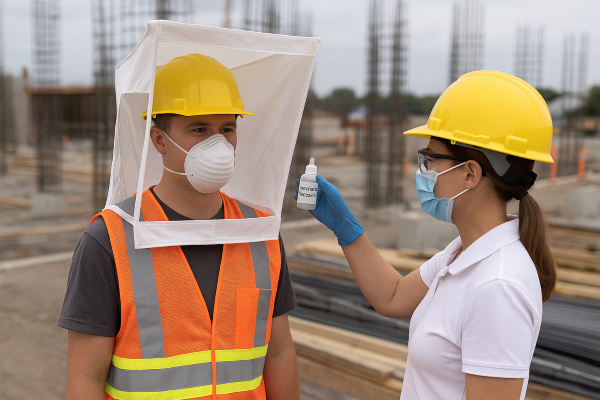
Fit, Training, and Maintenance Basics
Respiratory protection is only effective when it is used correctly. Poor fit or improper maintenance can significantly reduce its ability to protect.
Basic best practices include:
- Ensuring a proper seal and fit
- Replacing filters and cartridges as recommended
- Storing equipment in clean, dry conditions
- Providing basic training on correct usage
Regular checks and proper handling help extend the life of equipment and maintain its effectiveness.
Proper fit is critical, which is why respirator fit testing plays a key role in ensuring protection.
Building a Safer Workplace with Better Air Protection
Respiratory and air safety is an essential part of protecting worker health. Airborne hazards are often hidden, but the impact of long-term exposure can be serious.
By understanding common risks, choosing appropriate respiratory protection, and following basic safety practices, workplaces can reduce exposure and support long-term health.
Continue with these related guides:
Gas monitors and air detection devices
Types of respirators and when to use them






